About Bridle
Bridle demonstrate the integration of TiaC Systems support in open source projects, like the Zephyr Project, with libraries and source code for applications. It is a combination of software developed by TiaC Systems and open source projects, hosted as Git repositories in the DevZone or the Zephyr GitHub organization.
Every Bridle release consists of a combination of all those repositories
at different revisions. See the Repositories and revisions section for
a comprehensive list of repositories and their current revisions.
The revision of each of those repositories is determined by the current
revision of the main (manifest) repository, tiac-bridle, which contains
the Bridle manifest file that helps manage the repositories as one
code base with the West Tool tool.
About the Bridle license
Licenses are located close to the source files. You can find a LICENSE file, containing the details of the license, at the top of every Bridle repository. Each file included in the repositories also has an SPDX identifier that mentions this license.
If a folder or set of files is open source and included in Bridle under its
own license (for example, any of the Apache or MIT licenses), it will have
either its own LICENSE file included in the folder or the license
information embedded inside the source files themselves.
The SPDX tool is used to generate license reports on each release of the Bridle. You can also use SPDX to generate license reports for your projects that are specific to the code included in your application.
Documentation pages
The documentation consists of several inter-linked documentation sets, one for each repository. You can switch between these documentation sets by using the selector in the bottom-left corner of each page.
The entry point is the Bridle documentation that you are currently reading. The local Zephyr documentation is a slightly extended version of the official Zephyr Project documentation, containing some additions specific to TiaC Systems.
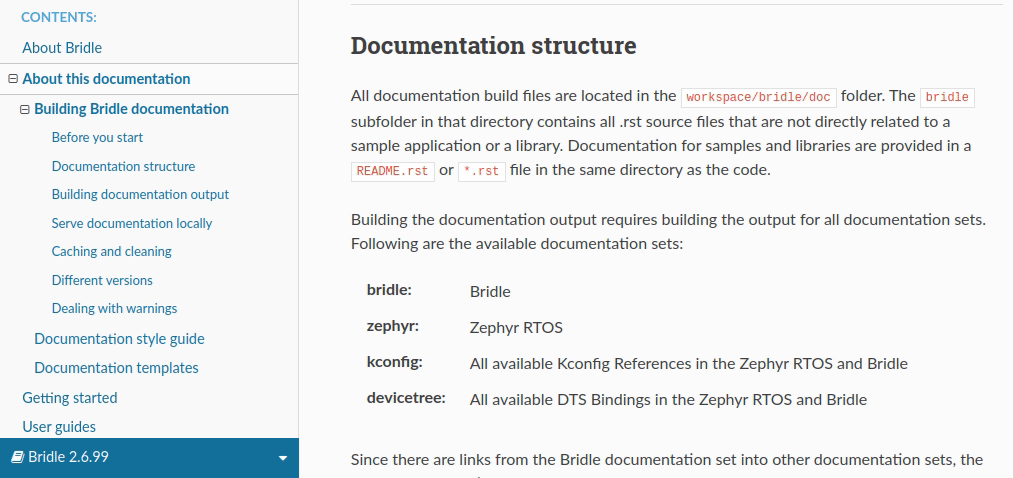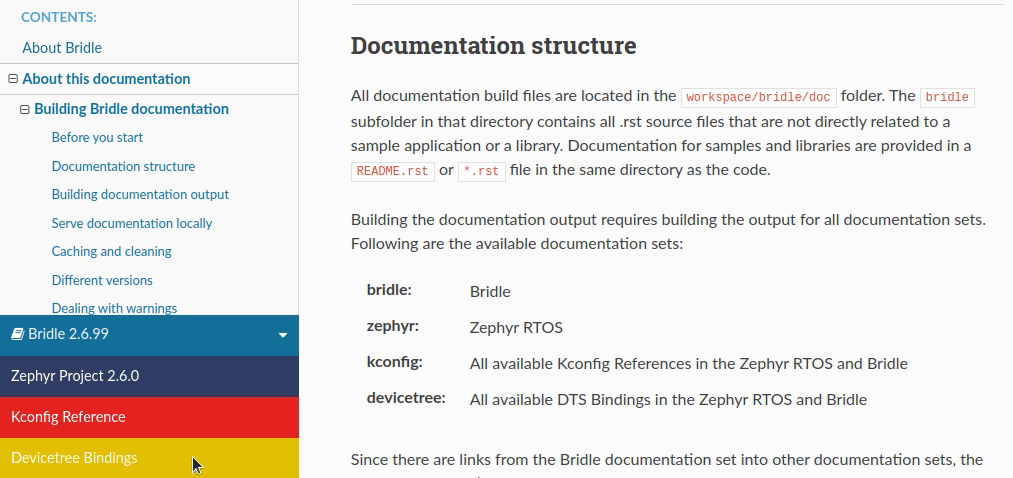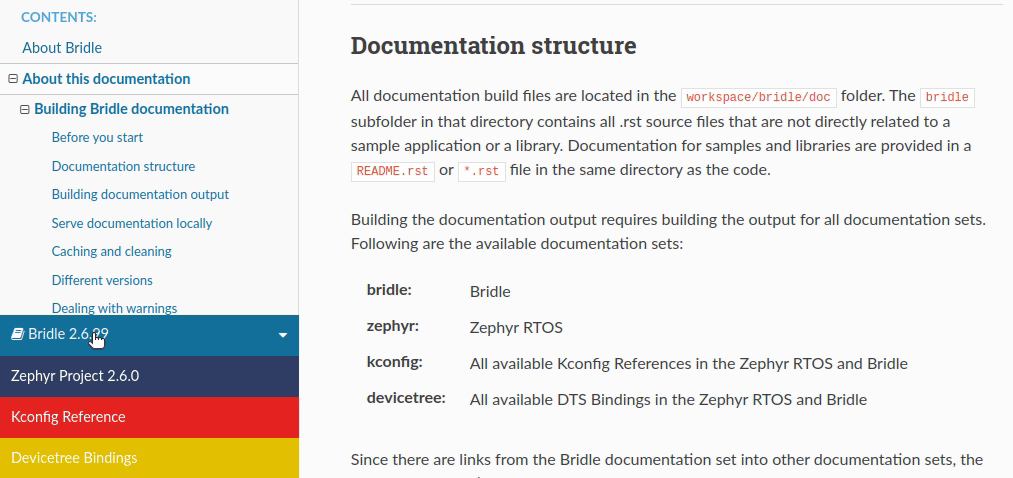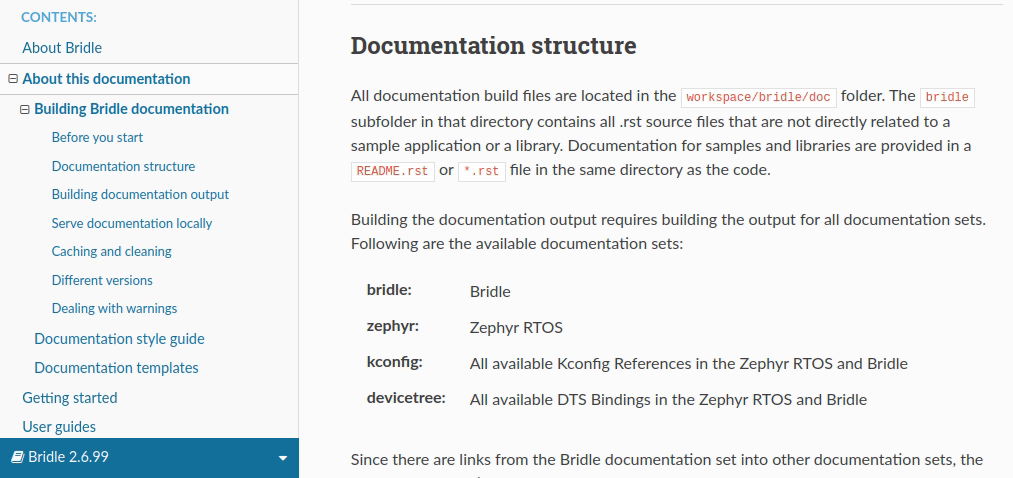
Bridle documentation set selector
The Bridle documentation contains all information that is specific to the Bridle and describes our libraries, samples, and applications. The API documentation is extracted from the source code and included with the library documentation.
For instructions about building the documentation locally, see Building Bridle documentation. For more information about the documentation conventions and templates, see About this documentation.
Tools and configuration
The figure below visualizes the tools and configuration methods in the Bridle. They are based on the Zephyr Project. All of them have a role in the creation of an application, from configuring the libraries or applications to building them.
Bridle tools and configuration methods
Configuration System (Kconfig) generates definitions that configure libraries and subsystems. See also the Kconfig language.
Devicetree describes the hardware. See also the Devicetree reference.
CMake generates build files based on the provided
CMakeLists.txtfiles, which use information from Kconfig and devicetree. See the CMake documentation.Ninja (comparable to make) uses the build files to build the program, see the Ninja documentation.
The GCC compiler creates the executables.
Git Tool
Git is a free and open source distributed version control system that allows managing the changes in the code or other collections of information (set of files) over time.
Git organizes data (files or directories) in project repositories. The data is managed like a series of snapshots. Every time you commit, or save the state of your project, Git takes a snapshot of what the files look like at that exact moment and stores a reference to that snapshot. For unchanged files, Git provides just a link to the previous identical file it has already stored.
Git offers a lot of flexibility in how users manage changes, and repositories are easily duplicated. In Bridle, forking is the agreed-upon Git workflow. To contribute, the official public repository in GitHub is forked.
When you say you are forking a repository, you are creating a copy of the repository under your GitHub ID. This means that you are creating an identical copy that might diverge from the original over time. This copy is your personal public repository that nobody else is allowed to push to, but changes can be pulled from it.
The original repository is called the upstream repository, and the newly created copy the downstream repository. Any changes made to the original repository are reflected back to your forked repositories by using fetch and rebase commands.
A git clone command is used to get a copy of your downstream repository onto your local machine. This serves as a private development environment.
Local commits are pushed to your own downstream repository, and not the official one. To integrate the changes into the main upstream repository, a pull request is created explicitly. Before it is merged, the pull request also serves as a convenient discussion thread if there are issues with the contributed code. If your pull request is approved, the changes are merged with the existing original content. Until then, your changes are reflected only in the copy you forked.
A fork can be hosted on any server, including a public Git hosting site like GitHub. It is, however, important to differentiate between the generic concept of a fork and GitHub’s concept of a GitHub fork. When you create a GitHub fork, GitHub copies the original repository and tags the downstream repository (the fork) with a flag that allows users to send pull requests from the fork to its upstream repository. GitHub also supports creating forks without linking them to the upstream respository. See the GitHub documentation for information about how to do this.
Everything in Git is checksummed before it is stored and is then referred to by that checksum. The mechanism that Git uses for this checksumming is called a SHA-1 hash. This hash is a 40-character string, composed of hexadecimal characters (0–9 and a–f), and calculated based on the contents of a file or directory structure in Git.
West Tool
The Zephyr project includes a tool called west. The Bridle uses west to manage the combination of multiple Git repositories and versions.
Some of west’s features are similar to those provided by Git Submodules and Google’s Repo tool. But west also includes custom features required by the Zephyr Project that were not sufficiently supported by the existing tools. For more details about the reasons behind the introduction of west, see the History and Motivation section of the Zephyr documentation.
West’s workspace contains exactly one
manifest repository, which is a main Git repository
containing a west manifest file. Additional Git repositories in the workspace
managed by west are called projects. The manifest repository controls which
commits to use from the different projects through the manifest file. In the
Bridle, the main repository tiac-bridle contains a west manifest file
west.yml, that determines the revision of all other repositories
and that is complete different from Zephyr’s west manifest file
west.yml. This means that tiac-bridle acts as the manifest
repository, while the other repositories are projects, like Zephyr in the case
of Bridle. When developing in the Bridle, your application will use
libraries and features from folders that are cloned from different repositories
or projects. The west tool keeps control of which commits to use from the
different projects. It also makes it fairly simple to add and remove modules.
Some west commands are related to Git commands with the same name, but operate on the entire west workspace. Some west commands take projects as arguments. The two most important workspace-related commands in west are west init and west update. The west init command creates a west workspace, and you typically need to run it only once to initialize west with the revision of the Bridle that you want to check out. It clones the manifest repository into the workspace. However, the content of the manifest repository is managed using Git commands, since west does not modify or update it. To clone the project repositories, use the west update command. This command makes sure your workspace contains Git repositories matching the projects defined in the manifest file. Whenever you check out a different revision in your manifest repository, you should run west update to make sure your workspace contains the project repositories the new revision expects (according to the manifest file).
For more information about west init, west update, and other built-in commands, see Built-in commands. For more information about the west tool, see the West (Zephyr’s meta-tool) user guide.
See Getting started for information about how to install Bridle and about the first steps. See Development model for more information about the Bridle code base and how to manage it.
Repositories and revisions
The following table lists all the repositories (and their respective revisions) that are included as part of Bridle v3.6.1 release:
Project |
Revision |
|---|---|
zephyr |
|
ubxlib |
|
canopennode |
|
chre |
|
psa-arch-tests |
|
tf-m-tests |
|
cmsis |
|
edtt |
|
fatfs |
|
hal_altera |
|
hal_atmel |
|
hal_espressif |
|
hal_gigadevice |
|
hal_infineon |
|
hal_microchip |
|
hal_nordic |
|
hal_nuvoton |
|
hal_nxp |
|
hal_openisa |
|
hal_quicklogic |
|
hal_renesas |
|
hal_rpi_pico |
|
hal_silabs |
|
hal_st |
|
hal_stm32 |
|
hal_telink |
|
hal_ti |
|
hal_xtensa |
|
libmetal |
|
liblc3 |
|
littlefs |
|
loramac-node |
|
lvgl |
|
mbedtls |
|
mcuboot |
|
mipi-sys-t |
|
net-tools |
|
open-amp |
|
openthread |
|
picolibc |
|
segger |
|
tinycrypt |
|
trusted-firmware-m |
|
trusted-firmware-a |